Kinematics is the branch of dynamics concerned with the description of motion.
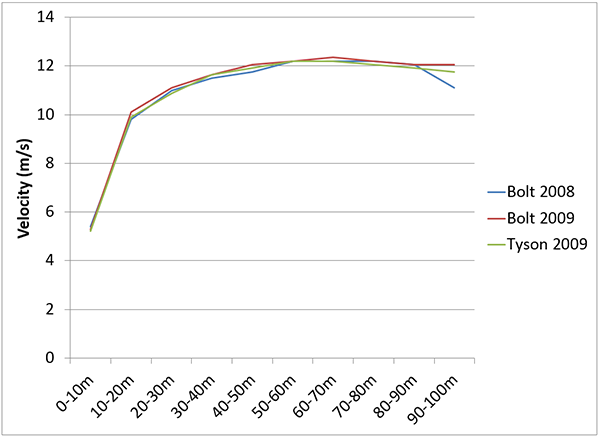
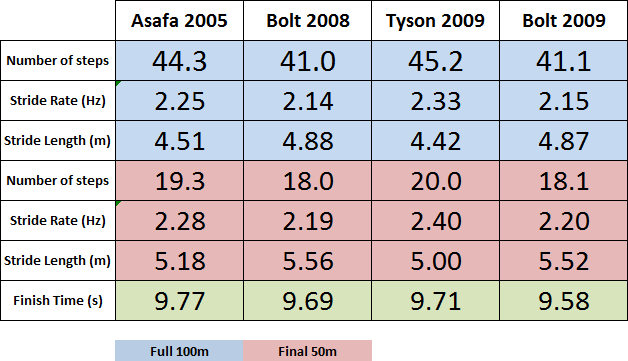
Data from some of the fastest races ever

Bolt's top speed 12.35 m/s (27.6 mph)
Rectilinear Translation-All points on the object move the same distance in a straight line.
Angular or Rotary Motion: All points along a curve about a fixed line or axis.
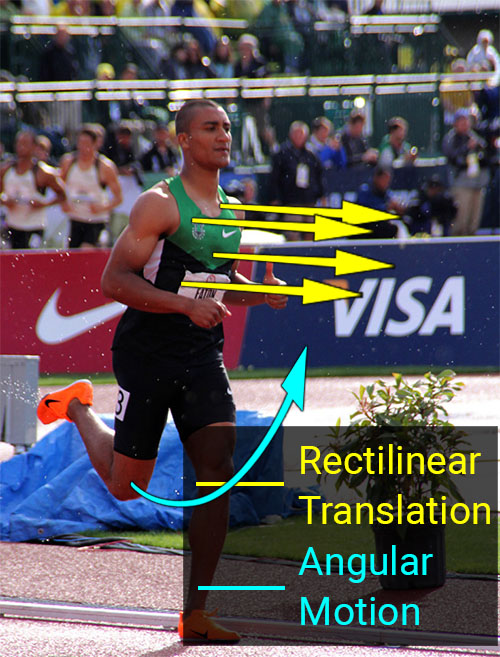
Curvilinear Translation-All points move so that the orientation of the object does not change and all points on the object move along a curve.
General Motion
x, y, z, rotationx, rotationy, rotationz
Slope of a position-time graph
SPEED vs VELOCITY
\(Speed = {Distance \over ΔTime}\)
What was a marathon runner's average speed in finishing the race in 2 hours 11 minutes?
A rowing shell was progressing upstream in the Willamette River at 8 mph relative to the water, while the river was flowing at 1 mph. What was the velocity of the shell with respect to the riverbank?
| 500m Splits for 2000m Race | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Split | Estimated | With 1 m/s current | With -1 m/s current |
| 500m | 2:00 | 1:37 | 2:38 |
| 1000m | 4:00 | 3:14 | 5:16 |
| 1500m | 5:00 | 4:50 | 7:54 |
| 2000m | 6:00 | 6:27 | 10:32 |
What combinations of velocity and acceleration are possible?
What does this imply for running around a curve?
Is someone accelerating when running a constant speed around a curve?
Shot Put Example
Displacement with intial velocity and with constant acceleration
d=vit + 0.5at2
Skeleton Example

(Garrett A. Wollman) copyright 2017 ("CC BY-SA 4.0 license")
What is the average speed if you swim 1500m at 1.46 m/s, bike 40 km at 11.27 m/s, and run 10 km at 5.72 m/s? (2012 Olympic Triathlon)