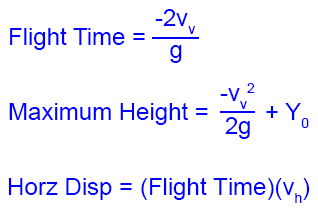
|
Projectile Motion
A Projectile is any body that has been set on its path by some force and continues in motion by its own inertia. (Gravity has a major effect on motion).
Examples of Projectiles include: Example 1, Example 2, Example 3, Example 4
Horizontal and vertical components are independent
Equations of motion for projectiles (Download video)
Demonstration on what happens as initial conditions are altered
|
A shot put is released with a velocity of \(14 {m \over s}\) at an angle of \(42^o\). What are the vertical and horizontal components of velocity? (Article example)
|