 |
Wolff's law: A tissue adapts to the level of stress imposed on it; the level of adaptation in a tissue reflects the level of typical loading
Where does Wolff's law fail?
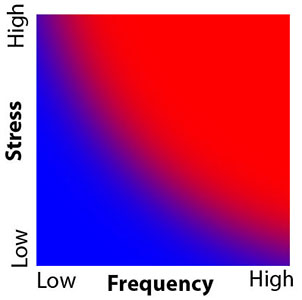
Can this curve be altered? How?
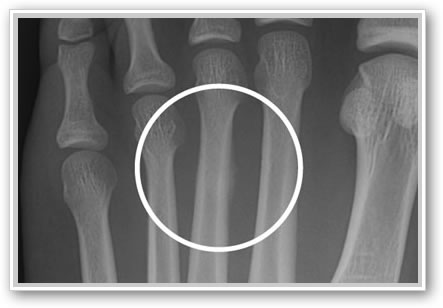

What type of stress causes injury?
Yield stress: 153 MPa Yield strain: 0.009 or 0.9% Young's Modulus: 17 GPa
Ultimate stress: 165 MPa Ultimate strain: 0.032 or 3.2% |
Bone
|
Tendon and ligament
|
| Tension | Compression | Shear | ||
| Compact Bone | Stress (MPa) | 90-170 | 100-280 | 50-100 |
| Strain (%) | 0.7-5 | 1-2.4 | ||
| Ligament | Stress (MPa) | 1-2 | ||
| Strain (%) | 30-125 | |||
| Tendon | Stress (MPa) | 15-100 | ||
| Strain (%) | 10-17 | |||
Intrinsic and extrinsic factors related to injury development
Model for overuse injuries
Within-activity cross-training
Using biomechanical analyses to prevent injury